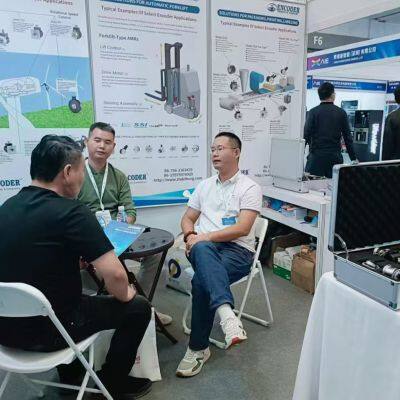
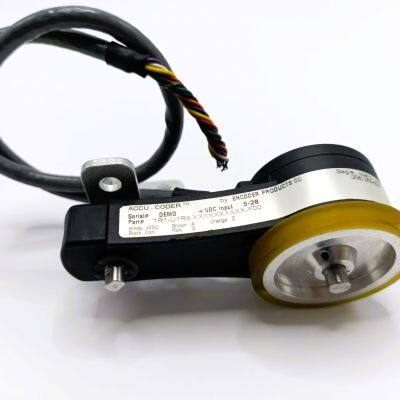
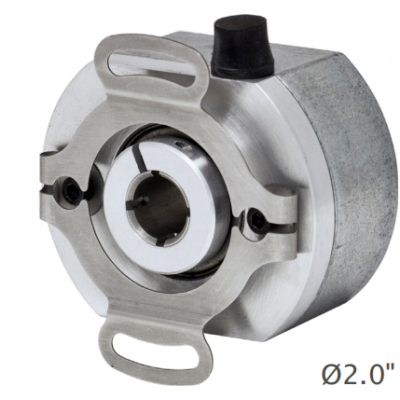
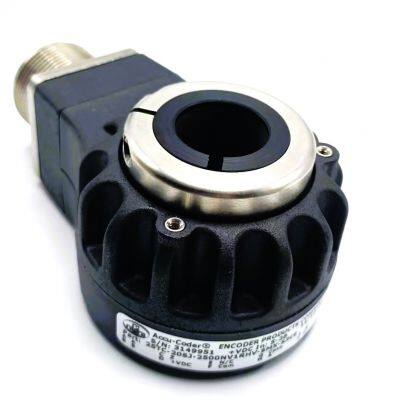
The encoder is used in the robotics industry
The encoder is used in the robotics industry
Encoders have a wide and critical application in the robotics industry.
1.Joint angle measurement and position control: Encoders are installed at each joint of the robot, which can monitor the rotational angle of the joints in real-time, converting mechanical rotation angles into electronic signals, providing the control system with precise position data.

Application example: Industrial robots perform high-precision tasks, such as the assembly of components in automobile manufacturing, by accurately measuring joint angles through encoders at the joints, ensuring that the robot's arm can precisely reach the designated position to pick up and place components, achieving high-precision assembly tasks.
2.Speed control: The encoder provides precise speed feedback to the control system by real-time monitoring of the robot's motion speed. The control system adjusts the robot's motion speed in real time based on the output signals from the encoder.

Application example: In a logistics warehouse, mobile robots need to shuttle between shelves at different speeds for goods handling. Encoders monitor the robot's driving speed in real-time, and when the robot approaches a shelf or encounters an obstacle, the control system reduces the speed based on the encoder's feedback signal to achieve safe, accurate docking and operation; when driving in open corridors, the speed is increased to enhance handling efficiency.
3.Synchronous control: In multi-joint robots or multi-axis motion control systems, the control system can determine the positional differences between different joints or components by comparing the output signals of the encoders, and adjust their movement speeds to ensure synchronous motion. Application example: In some large welding robot workstations, multiple robotic arms need to work together to weld large workpieces. Through encoder synchronous control, it ensures that each robotic arm can move synchronously along the predetermined trajectory and speed, guaranteeing welding quality and precision.
4.Fault diagnosis and maintenance: By monitoring the output signal of the encoder in real time, the control system can determine whether the robot has any faults or abnormal conditions. For example, when the encoder's output signal is abnormal, it may indicate issues such as looseness, wear, or damage at the robot's joints. Application example: During the long-term operation of the robot, the encoder continuously monitors the motion state of the joints. If the feedback signal from an encoder at a particular joint shows abnormal fluctuations or deviations, the control system can promptly issue a fault alarm, alerting maintenance personnel to inspect and repair that joint, preventing further faults and enhancing the robot's reliability and lifespan.